Main Structures and Summary of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a multi-step process that requires specific wavelengths of visible sunlight, carbon dioxide (which is low in energy), and water as substrates (Figure). After the process is complete, it releases oxygen and produces glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA3P), as well as simple carbohydrate molecules (high in energy) that can then be converted into glucose, sucrose, or any of dozens of other sugar molecules. These sugar molecules contain energy and the energized carbon that all living things need to survive.
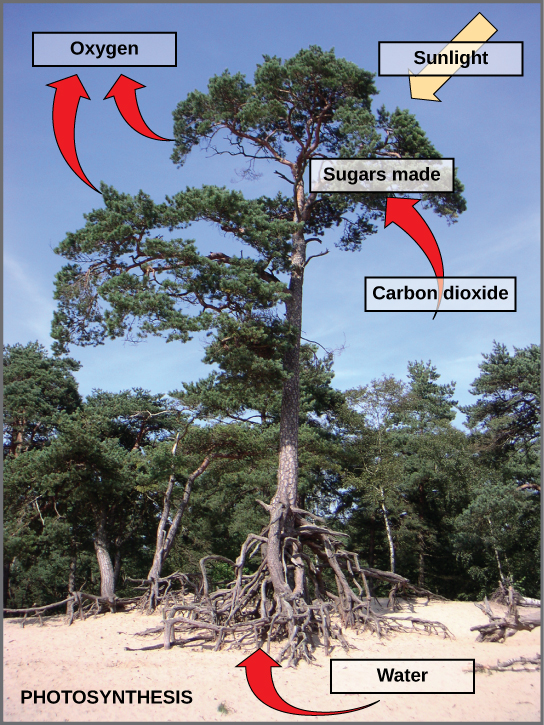
The following is the chemical equation for photosynthesis (Figure):
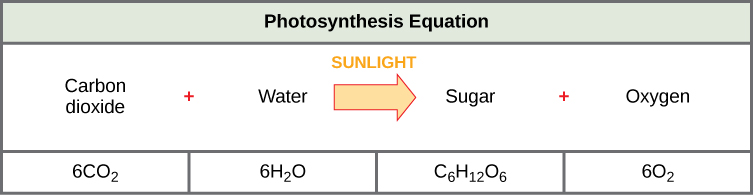
Although the equation looks simple, the many steps that take place during photosynthesis are actually quite complex. Before learning the details of how photoautotrophs turn sunlight into food, it is important to become familiar with the structures involved.