By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Understand the nutritional adaptations of plants
Describe mycorrhizae
Explain nitrogen fixation
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 09/21/2018

By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Understand the nutritional adaptations of plants
Describe mycorrhizae
Explain nitrogen fixation
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe how plants obtain nutrients
List the elements and compounds required for proper plant nutrition
Describe an essential nutrient
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe how soils are formed
Explain soil composition
Describe a soil profile
Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Explain how the binding of a ligand initiates signal transduction throughout a cell
Recognize the role of phosphorylation in the transmission of intracellular signals
Evaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe how signaling pathways direct protein expression, cellular metabolism, and cell growth
Identify the function of PKC in signal transduction pathways
Recognize the role of apoptosis in the development and maintenance of a healthy organism
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe four types of signaling mechanisms found in multicellular organisms
Compare internal receptors with cell-surface receptors
Recognize the relationship between a ligand’s structure and its mechanism of action
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe how single-celled yeasts use cell signaling to communicate with one another
Relate the role of quorum sensing to the ability of some bacteria to form biofilms
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe how cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell growth
Understand how proto-oncogenes are normal cell genes that, when mutated, become oncogenes
Describe how tumor suppressors function
Explain how mutant tumor suppressors cause cancer
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes
Distinguish between chromosomes, genes, and traits
Describe the mechanisms of chromosome compaction
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell
Explain how the three internal “control checkpoints” occur at the end of G1, at the G2/M transition, and during metaphase
Describe the molecules that control the cell cycle through positive and negative regulation
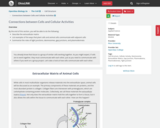
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe the process of binary fission in prokaryotes
Explain how FtsZ and tubulin proteins are examples of homology
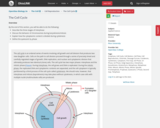
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe the three stages of interphase
Discuss the behavior of chromosomes during karyokinesis/mitosis
Explain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesis
Define the quiescent G0 phase
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe the extracellular matrix
List examples of the ways that plant cells and animal cells communicate with adjacent cells
Summarize the roles of tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and plasmodesmata
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
Describe the structure of eukaryotic cells
Compare animal cells with plant cells
State the role of the plasma membrane
Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles