- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 06/29/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Show the relationship between production costs and comparative advantage
Identify situations of mutually beneficial trade
Identify trade benefits by considering opportunity costs
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain the aggregate supply curve and how it relates to real GDP and potential GDP
Explain the aggregate demand curve and how it is influenced by price levels
Interpret the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model
Identify the point of equilibrium in the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model
Define short run aggregate supply and long run aggregate supply
In this chapter, you will learn about:
Macroeconomic Perspectives on Demand and Supply
Building a Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Shifts in Aggregate Supply
Shifts in Aggregate Demand
How the AD/AS Model Incorporates Growth, Unemployment, and Inflation
Keynes’ Law and Say’s Law in the AD/AS Model
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain merchandise trade balance, current account balance, and unilateral transfers
Identify components of the U.S. current account balance
Calculate the merchandise trade balance and current account balance using import and export data for a country
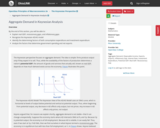
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain real GDP, recessionary gaps, and inflationary gaps
Recognize the Keynesian AD/AS model
Identify the determining factors of both consumption expenditure and investment expenditure
Analyze the factors that determine government spending and net exports
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Contrast traditional economies, command economies, and market economies
Explain gross domestic product (GDP)
Assess the importance and effects of globalization