- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 06/29/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Analyze whether monetary policy decisions should be made more democratically
Calculate the velocity of money
Evaluate the central bank’s influence on inflation, unemployment, asset bubbles, and leverage cycles
Calculate the effects of monetary stimulus
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain merchandise trade balance, current account balance, and unilateral transfers
Identify components of the U.S. current account balance
Calculate the merchandise trade balance and current account balance using import and export data for a country
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Identify three ways in which borrowing money or running a trade deficit can result in a healthy economy
Identify three ways in which borrowing money or running a trade deficit can result in a weaker economy
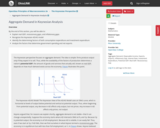
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain real GDP, recessionary gaps, and inflationary gaps
Recognize the Keynesian AD/AS model
Identify the determining factors of both consumption expenditure and investment expenditure
Analyze the factors that determine government spending and net exports
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Evaluate the Keynesian view of recessions through an understanding of sticky wages and prices and the importance of aggregate demand
Explain the coordination argument, menu costs, and macroeconomic externality
Analyze the impact of the expenditure multiplier
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Contrast nominal GDP and real GDP
Explain GDP deflator
Calculate real GDP based on nominal GDP values

By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Explain the importance of potential GDP in the long run
Analyze the role of flexible prices
Interpret a neoclassical model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply
Evaluate different ways for measuring the speed of macroeconomic adjustment