- Subject:
- U.S. History
- Material Type:
- Module
- Provider:
- Ohio Open Ed Collaborative
- Tags:
- License:
- Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial
- Language:
- English
- Media Formats:
- eBook, Text/HTML
Chapter 2 – European Encounters with the New World
Openstax Chapter 1-The Americas, Europe, and Africa Before 1492
The American Yawp- Chapter 1 Primary sources
The American Yawp- Chapter One
The America Yawp – Chapter 3: British North America
U. S. History: West African Society at the Point of contact
West Africa and the Role of Slavery
The Americas, Europe and Africa before 1492
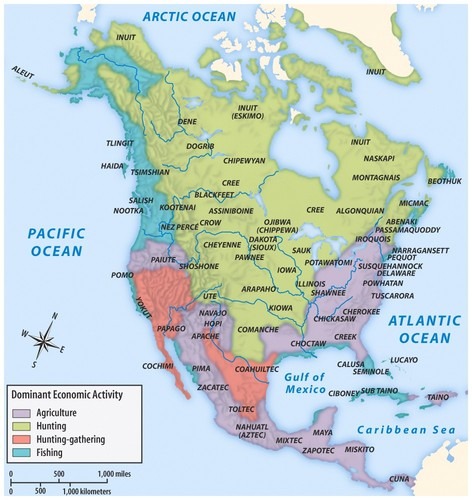
Overview
What Europeans called “the New World” had people living there that had been there for thousands of years. Great civilizations had risen, large population centers had come and gone, and the people we know today as Native Americans or First Americans spoke many languages, had trade routes, treaties, and a variety of religions.
Africa, or more specifically, West Africa, also had great kingdoms, trade routes, and a large variety of languages, religions, and traditions. Many West Africans had already encountered European and Middle Eastern peoples through trade along the sea ports and across the Mediterranean.
As religious and social turmoil changed the European landscape, new inventions like the caravel, astrolabe and compass allowed for easier and safer sea travel. Spain and Portugal led the search for an easier route to the Far East and discovered the New World. They were quickly followed by the French and British. Soon the Columbian Exchange would bring changes to the New World that no one could have expected, or predicted.
Learning Objectives
- Compare and Contrast the Mesoamerican civilizations, the North American civilizations, and Caribbean Islanders.
- Describe the geographical necessities when developing large population clusters.
- Describe the impact of religion in developing and maintaining societies in the Americas.
- Describe how commerce and conversion in Europe encouraged exploration into the Americas.
- Analyze the impact of religious conflict (Catholicism, Protestantism, and Islam) on the social authorities of Europe.
- Explain how technological inventions encouraged exploration and conquest.
- Compare and contrast Muslim slavery to European indentured servitude.
- Describe the major West African kingdoms religions, political structure, and family structure.
- Explain the role of slavery in West African Kingdoms and the Islamic Empire.
Textbook Readings
Many of these text books are similar, but each has it's own style. Find the one that you like the best, with the exception of the last one, which is the only text that tells about West Africa.
Openstax US History
The American Yawp-
History in the Making: A History of the People of the United States of America to 1877 –
Boundless U.S. History –
U. S. History
Module Supplemental Readings/Videos
Exploring the Early Americas - (Library of Congress Exhibit)
The Cultures and History of the Americas: The Jay I. Kislak Collection at the Library of Congress
The Black Legend, Native Americans, and Spaniards Crash Course U.S. History # 1
West Africa and the Role of Slavery http://www.pbs.org/wonders/Episodes/Epi3/slave_2.htm https://www.blackpast.org/global-african-history/songhai-empire-ca-1375-1591/
The Americas
- Compare and Contrast the Mesoamerican civilizations, the North American civilizations, and Caribbean Islanders.
- Describe the geographical necessities when developing large population clusters.
- Describe the impact of religion in developing and maintaining societies in the Americas.
Europe on the Brink of Change
- Describe how commerce and conversion in Europe encouraged exploration into the Americas.
- Analyze the impact of religious conflict (Catholicism, Protestantism, and Islam) on the social authorities of Europe.
- Explain how technological inventions encouraged exploration and conquest.
West African Societies
- Compare and contrast Muslim slavery to European indentured servitude.
- Describe the major West African kingdoms religions, political structure, and family structure.
Glossary of Key Terms
Aztecs: Native American empire that controlled present-day Mexico through a system of trade and tribute, until 1521, when they were conquered by Spanish Hernán Cortés.
chinampas: "floating islands" utilized for intensive agricultural production.
conquistadors: people from Spain who conquered the Aztecs that came to America because of its riches and to convert people to Christianity
Incas: Highly advanced South American civilization that developed sophisticated agricultural techniques in present-day Peru until they were conquered by Spanish forces under Francisco Pizarro in 1532.
Maya: A Mesoamerican civilization noted for its sophisticated and highly developed writing system that encompassed southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador.
Reconquista: Spain's effort to take back its land from the Moors; it lasted about 800 years from 711 to 1492
quipu: an arrangement of knotted strings on a cord, used by the Inca to record numerical information.
Instructor Resources
Arrange students into small groups. Have each group create a chart similar to the following
| Native American | West African | European | |
| religion | |||
| family | |||
| politics | |||
| economics | |||
Each group of students should list the types of each for each people group. For example, religion for the Native Americans, West Africans, and Europeans, to compare similarities and differences between each people group.