Lesson 1
Preface
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Subject:
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Tags:
-
- ADD
- ADHD
- Abnormal Motor Behavior
- Abnormal Psychology
- Abraham Maslow
- Absentmindedness
- Absolute Threshold
- Abu Ghraib
- Accommodation
- Acoustic Encoding
- Acquisition
- Action Potential
- Actor-observer Bias
- Addiction
- Adolescence
- Adrenal Gland
- Adrenarche
- Afterimage
- Ageism
- Aggression
- Agonist
- Agoraphobia
- Alarm Reaction
- Alfred Adler
- Algorithm
- All-or-none
- Allele
- Alpha Wave
- Altruism
- American Psychiatric Association
- American Psychological Association
- Americans With Disabilities Act
- Amnesia
- Amplitude
- Amygdala
- Anabolic Steroid
- Anal Stage
- Analytical Intelligence
- Analytical Psychology
- Anchoring Bias
- Anger
- Animal Research
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Antagonist
- Anterograde Amnesia
- Antisocial
- Antisocial Personality Disorder
- Anxiety Disorder
- Appraisal
- Archetype
- Archival Research
- Arousal
- Arousal Theory
- Artificial Concept
- Asch Effect
- Assimilation
- Associative Learning
- Asthma
- Asylum
- Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
- Attachments
- Attention
- Attention Deficit Disorder
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- Attitude
- Attraction
- Attribution
- Attrition
- Atypical
- Auditory Cortex
- Auditory System
- Authoritarian Parenting Style
- Authoritative Parenting Style
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Automatic Processing
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Availability Heuristic
- Aversive Conditioning
- Avoidance Personality Disorder
- Avoidant Attachment
- Axon
- B. F. Skinner
- BFOQ
- BMI
- Bad Stress
- Bandura
- Bariatric Surgery
- Basilar Membrane
- Basolateral Complex
- Behavior Modification
- Behavior Therapy
- Behavioral Genetics
- Behaviorism
- Bias
- Big Five Personality Traits
- Binaural Cue
- Binge Eating Disorder
- Binocular Cue
- Binocular Disparity
- Biofeedback
- Biological Psychology
- Biological Rhythm
- Biomedical Therapy
- Biopsychology
- Biopsychosocial Model
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar and Related Disorders
- Bisexual
- Blind Spot
- Blocking
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Body Language
- Body Mass Index
- Bona Fide Occupational Qualification
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Bottom-up Processing
- Brain
- Brain Imaging
- Brain Scan
- Broca's Area
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Bullying
- Bystander Effect
- C-TCB
- CPAP
- CT Scan
- Cannon-Bard
- Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
- Cardiovascular Disorder
- Careers in Psychology
- Carl Jung
- Carl Rogers
- Case Study
- Cataplexy
- Catatonic Behavior
- Causality
- Cause and Effect
- Cause-and-effect Relationship
- Central Nervous System
- Central Nucleus
- Central Route Persuasion
- Central Sleep Apnea
- Cerebellum
- Checklist
- Chemical Senses
- Chromosome
- Circadian Rhythm
- Classical Conditioning
- Client-centered Therapy
- Clinical Psychology
- Clinical Study
- Closure
- Cochlea
- Cochlear Implant
- Codeine
- Cognition
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy
- Cognitive Development
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Cognitive Empathy
- Cognitive Map
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Script
- Cognitive Therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral Therapy
- Cognitive-mediational Theory
- Collective Unconscious
- Collectivist Culture
- Color Vision
- Commission
- Comorbid Disorder
- Comorbidity
- Companionate Love
- Compliance
- Components of Emotion
- Compulsion
- Computerized Tomography
- Concept
- Conception
- Concrete Operational Stage
- Conditioned Response
- Conditioned Stimulus
- Conditioning
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- Cone
- Confederate
- Confidentiality
- Confirmation Bias
- Conformity
- Confounding Variable
- Congenital Analgesia
- Congenital Deafness
- Congenital Insensitivity to Pain
- Congruence
- Conscious
- Consciousness
- Conservation
- Constrict
- Construction
- Consummate Love
- Contemporary Psychology
- Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks Test
- Continuity
- Continuous Development
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
- Continuous Reinforcement
- Control Group
- Convergent Thinking
- Coping
- Coping With Stress
- Cornea
- Corpus Callosum
- Correlation
- Correlation Coefficient
- Correlational Research
- Cortisol
- Counseling Psychology
- Counterconditioning
- Couples Therapy
- Creative Intelligence
- Creativity
- Crest
- Critical (sensitive) Period
- Cross-sectional Research
- Crystallized Intelligence
- Cultural Competence
- Cultural Display Rule
- Cultural Intelligence
- Culture
- Cyberbullying
- DARE
- DNA
- DNR
- DSM
- DSM-5
- Daily Hassles
- Darwin
- De Novo Mutations
- Deaf Culture
- Deafness
- Death
- Debriefing
- Deception
- Decibel
- Declarative Memory
- Deductive Reasoning
- Defense Mechanism
- Deinstitutionalization
- Delta Wave
- Delusion
- Dendrite
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- Dependent Personality Disorder
- Dependent Variable
- Depersonalization Disorder
- Depressant
- Depression
- Depressive Disorder
- Depth Perception
- Derealization Disorder
- Developmental Milestones
- Developmental Psychology
- Diagnosis
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- Diathesis-stress Model
- Difference Threshold
- Dilated
- Discontinuous Development
- Discrimination
- Disorganized Attachment
- Disorganized Motor Behavior
- Disorganized Thinking
- Displacement
- Dispositional
- Dissertation
- Dissociative Amnesia
- Dissociative Disorder
- Dissociative Fugue
- Dissociative Identity Disorder
- Distorted Body Image
- Distress
- Divergent Thinking
- Do Not Resuscitate
- Dominant Allele
- Dopamine Hypothesis
- Dorothea Dix
- Double-blind Study
- Downsizing
- Dream Analysis
- Drive Theory
- Drug Abuse
- Drug Abuse Resistance Education
- Drug Addiction
- Drug Use
- Dying
- Dysgraphia
- Dyslexia
- EEG
- Eating
- Eating Disorder
- Effortful Processing
- Ego
- Egocentrism
- Elaboration Likelihood Model
- Elaborative Rehearsal
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- Electroencephalography
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Embryo
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotion
- Emotion-focused Coping
- Emotional Expression
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy
- Empirical
- Empiricism
- Employment
- Encoding
- Endocrine System
- Engram
- Epigenetics
- Episodic Memory
- Equipotentiality Hypothesis
- Eric Erikson
- Erik Erikson
- Ethics
- Etiology
- Euphoric High
- Eustress
- Event Schema
- Evidence Based Practice
- Evolution
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Excitement
- Experimental Group
- Experimenter Bias
- Explicit Memory
- Exposure Therapy
- Extinction
- Extrinsic Motivation
- Eyewitness
- FMRI
- Facial Expression
- Facial Feedback Hypothesis
- Fact
- False Correlation
- False Memory Syndrome
- Falsifiable
- Family Therapy
- Fear
- Feminist Psychology
- Fetal Development
- Fight or Flight
- Figure-ground Relationship
- Fine Motor Skills
- Five Factor Model
- Fixed Interval Schedule
- Fixed Ratio Schedule
- Flashback
- Flashbulb Memory
- Flight of Ideas
- Flow
- Fluid Intelligence
- Flynn Effect
- Foot-in-the-door Technique
- Forebrain
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgetting
- Formal Operational Stage
- Fovea
- Fraternal Twin
- Frederick Taylor
- Free Association
- Frequency
- Frontal Lobe
- Functional Fixedness
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Functionalism
- Fundamental Attribution Error
- Gender Dysphoria
- Gender Identity
- Gene
- General Adaptation Syndrome
- Generalize
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Generational Difference
- Genetic Environmental Correlation
- Genetics
- Genital Stage
- Genotype
- Gestalt
- Gestalt Psychology
- Glia
- Glial Cell
- Gonad
- Gonadarche
- Good Continuation
- Good Stress
- Grammar
- Grandiose Delusion
- Gross Motor Skills
- Group Polarization
- Group Therapy
- Groupthink
- Gustation
- Gyri
- HPA Axis
- Habit
- Hair Cell
- Hallucination
- Hallucinogen
- Hans Eysenck
- Hans Selye
- Happiness
- Harmful Dysfunction
- Hassles
- Hawthorne Effect
- Health Psychology
- Hearing
- Heart Attack
- Heart Disease
- Hemisphere
- Heritability
- Hertz
- Heterosexual
- Heterozygous
- Heuristic
- Hierarchy of Needs
- Higher-order Conditioning
- Hindbrain
- Hindsight Bias
- Hippocampus
- History of Psychology
- Histrionic Personality Disorder
- Hoarding Disorder
- Homelessness
- Homeostasis
- Homophily
- Homophobia
- Homosexual
- Homozygous
- Hopelessness Theory
- Hormone
- Hospice
- Hostile Aggression
- Hostility
- Human Factors Psychology
- Human Research
- Humanism
- Humanistic Therapy
- Hunger
- Hyperactivity Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Hypertension
- Hyperthymesia
- Hypnogram
- Hypnosis
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal Axis
- Hypothalamus
- Hypothesis
- I-O Psychology
- IACUC
- ICD
- ID
- IRB
- Ideal Self
- Identical Twin
- Illusory Correlation
- Imitation
- Immune System
- Immunosuppression
- Immutable Characteristics
- Implicit Memory
- In-group
- In-group Bias
- Inattentional Blindness
- Incarceration
- Incongruence
- Incus
- Independent Variable
- Individual Psychology
- Individual Therapy
- Individualistic Culture
- Inductive Reasoning
- Industrial Organizational Psychology
- Industrial Psychology
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Industrial-organizational (I-O)
- Inferiority Complex
- Inflammatory Pain
- Informational Social Influence
- Informed Consent
- Initiation
- Insomnia
- Instinct
- Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
- Institutional Review Board
- Instrumental Aggression
- Intake
- Intelligence Quotient
- Inter-rater Reliability
- Interaural Level Difference
- Interaural Timing Difference
- Interference
- Internal Factor
- International Classification of Diseases
- Interpersonal
- Interview
- Intrapersonal
- Intrinsic Motivation
- Introspection
- Involuntary Treatment
- Iris
- Ivan Pavlov
- James-Lange
- James-Lange Theory of Emotion
- Jean Piaget
- Jet Lag
- Job Analysis
- Job Application
- Job Burnout
- Job Satisfaction
- Job Strain
- Job Training
- John Watson
- Julian Rotter
- Just Noticeable Difference
- Just-world Hypothesis
- K-complex
- Karen Horney
- Kinesthesia
- Kinsey
- Kitty Genovese
- Kurt Koffka
- LGBT
- LTM
- Language
- Latency Period
- Latent Content
- Latent Learning
- Law of Effect
- Lawrence Kohlberg
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning
- Lens
- Leptin
- Lexicon
- Light Wave
- Lillian Gilbreth
- Limbic System
- Linear Perspective
- Locus Coeruleus
- Locus of Control
- Long-term Memory
- Longitudinal Fissure
- Longitudinal Research
- Lucid Dream
- Lymphocyte
- MBTI
- MMPI
- MRI
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Malleus
- Mania
- Manic Episode
- Manifest Content
- Marijuana
- Martin Seligman
- Maslow
- Masters and Johnson
- Max Wertheimer
- Medical Marijuana
- Meditation
- Medulla
- Meissner’s Corpuscle
- Melatonin
- Membrane Potential
- Memory
- Memory Consolidation
- Memory Errors
- Memory Sins
- Memory-enhancing Strategy
- Mental Disorders
- Mental Health
- Mental Set
- Mentoring
- Merkel’s Disk
- Meta-analysis
- Metabolic Rate
- Methadone
- Methadone Clinic
- Methamphetamine
- Midbrain
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory
- Misattribution
- Misinformation Effect Paradigm
- Mitosis
- Mnemonic
- Mnemonic Device
- Modality
- Model
- Modern Psychology
- Molaison
- Monaural Cue
- Mood Disorder
- Morbid Obesity
- Morpheme
- Motivation
- Motor Cortex
- Motor Skills
- Multicultural Psychology
- Multiple Intelligences Theory
- Mutation
- Myelin Sheath
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
- Ménière's Disease
- Müller-Lyer
- NREM
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Narcolepsy
- Natural Concept
- Natural Selection
- Naturalistic Observation
- Nature
- Nature vs. Nurture
- Negative Affectivity
- Negative Correlation
- Negative Punishment
- Negative Reinforcement
- Negative Symptom
- Nervous System
- Neurodevelopmental Disorder
- Neuron
- Neuropathic Pain
- Neuroscience
- Neurosis
- Neurotransmitter
- Neutral Stimulus
- Newborn Reflexes
- Night Terror
- Noam Chomsky
- Nociception
- Nociceptor
- Non-REM
- Nondirective Therapy
- Normative Approach
- Normative Social Influence
- Norming
- Nurture
- O*Net
- OCD
- OCD Circuit
- Obedience
- Obese
- Object Permanence
- Observational Learning
- Observer Bias
- Obsession
- Obsessive-compulsive Disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive Personality Disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive and Related Disorders
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Occipital Lobe
- Occupational Stress
- Olfactory Bulb
- Olfactory Receptor
- Operant Conditioning
- Operational Definition
- Opiate
- Opinion
- Opioid
- Opponent-process Theory of Color Perception
- Optic Chiasm
- Optic Nerve
- Optimism
- Oral Stage
- Organizational Culture
- Organizational Psychology
- Orgasm
- Out-group
- Overgeneralization
- Overweight
- PET Scan
- PTSD
- Pacinian Corpuscle
- Pain
- Pancreas
- Panic Attack
- Panic Disorder
- Paranoid Delusion
- Paranoid Personality Disorder
- Parasomnia
- Parietal Lobe
- Partial Reinforcement
- Participant
- Pattern Perception
- Pavlov
- Peak
- Peer-reviewed Journal Article
- Perceived Control
- Perception
- Perceptual Hypotheses
- Performance Appraisal
- Performance Review
- Peripartum-onset Depression
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Peripheral Route Persuasion
- Permissive Parenting Style
- Persistence
- Persistent Depressive Disorder
- Personality
- Personality Assessment
- Personality Disorder
- Personality Psychology
- Personality Test
- Personality Trait
- Personality Type
- Persuasion
- PhD
- Phallic Stage
- Phenotype
- Pheromone
- Philip Zimbardo
- Phineas Gage
- Phobia
- Phoneme
- Photoreceptor
- Physical Dependence
- Physical Development
- Pineal Gland
- Pinna
- Pitch
- Pituitary Gland
- Place Theory of Pitch Perception
- Placenta
- Plateau
- Play Therapy
- Polygenic
- Polygraph
- Pons
- Population
- Positive Affect
- Positive Correlation
- Positive Psychology
- Positive Punishment
- Positive Reinforcement
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Postdoctoral Training Program
- Postpartum Depression
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Practical Intelligence
- Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Prefrontal Cortex
- Prejudice
- Prenatal Care
- Prenatal Development
- Preoperational
- Primary Appraisal
- Primary Reinforcer
- Primary Sexual Characteristics
- Principle of Closure
- Proactive Interference
- Problem-focused Coping
- Problem-solving Strategy
- Procedural Justice
- Procedural Memory
- Prodromal Symptom
- Product Placement
- Projection
- Projective Test
- Proprioception
- Prosocial
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prototype
- Proximity
- PsyD
- Psyche
- Psychoanalysis
- Psychoanalyst
- Psychoanalytic Theory
- Psychobiology
- Psychodynamic Therapy
- Psychological Dependence
- Psychological Disorder
- Psychological Disorders
- Psychological Research
- Psychologists
- Psychology
- Psychology Careers
- Psychology Employment
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychopathology
- Psychophysiological Disorders
- Psychosexual Development
- Psychosexual Stages of Development
- Psychosocial Development
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotropic
- Punishment
- Pupil
- RBD
- REM
- REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
- RISB
- Racism
- Random Assignment
- Random Sample
- Range of Reaction
- Rapid Eye Movement
- Rational Emotive Therapy (RET)
- Rationalization
- Reaction Formation
- Real Self
- Recall
- Receptor
- Recessive Allele
- Reciprocal Determinism
- Reciprocity
- Recognition
- Reconstruction
- Reflex
- Refractory Period
- Regression
- Reinforcement
- Relapse
- Relationships
- Relaxation Response Technique
- Relearning
- Reliability
- Replication
- Representative Bias
- Representative Sample
- Repression
- Research
- Research Ethics
- Research Methods
- Research Regulation
- Resistant Attachment
- Resolution
- Response-based Stress
- Resting Potential
- Restless Leg Syndrome
- Reticular Formation
- Retina
- Retrieval
- Retroactive Interference
- Retrograde Amnesia
- Reuptake
- Reversibility
- Richard Rahe
- Rods
- Rogerian Therapy
- Role Schema
- Romantic Love
- Rorschach Inkblot Test
- Rotating Shift Work
- Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank
- Ruffini Corpuscle
- Rumination
- SCN
- SIDS
- SRRS
- STM
- Safety Behavior
- Sample
- Satiation
- Scapegoating
- Schachter-Singer
- Schachter-Singer Two-factor Theory of Emotion
- Schema
- Schemata
- Schiavo
- Schizoid Personality Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder
- Scientific Management
- Scientific Method
- Scientific Research
- Script
- Seasonal Pattern Depression
- Second-order Conditioning
- Secondary Appraisal
- Secondary Reinforcer
- Secondary Sexual Characteristics
- Secure Attachment
- Secure Base
- Selective Migration
- Self-concept
- Self-disclosure
- Self-efficacy
- Self-efficacy Abilities
- Self-fulfilling Prophecy
- Self-reference Effect
- Self-serving Bias
- Semantic Encoding
- Semantic Memory
- Semantics
- Semipermeable Membrane
- Sensation
- Sensation and Perception
- Senses
- Sensorimotor
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Sensory Adaptation
- Sensory Memory
- Set Point Theory
- Sex Drive
- Sexism
- Sexual Harassment
- Sexual Orientation
- Sexual Response Cycle
- Shaping
- Short-term Memory
- Sickle-cell Anemia
- Sigmund Freud
- Signal Detection Theory
- Similarity
- Single-blind Study
- Situational
- Skinner
- Skinner Box
- Sleep
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Debt
- Sleep Deprivation
- Sleep Disorders
- Sleep Problems
- Sleep Rebound
- Sleep Regulation
- Sleep Spindle
- Sleep Stages
- Sleepwalking
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Social Exchange Theory
- Social Facilitation
- Social Loafing
- Social Norm
- Social Psychology
- Social Readjustment Rating Scale
- Social Role
- Social Support
- Social-cognitive Theory
- Society for Industrial and Organizational
- Sociocultural Treatment
- Socioemotional Selectivity Theory
- Sodium-potassium Pump
- Solomon Asch
- Soma
- Somatic Delusion
- Somatic Nervous System
- Somatosensory Cortex
- Somatosensory System
- Somatotype
- Somnambulism
- Sound
- Sound Wave
- Specific Phobia
- Spermarche
- Spinal Cord
- Spontaneous Recovery
- Sport and Exercise Psychology
- Stage 1 Sleep
- Stage 2 Sleep
- Stage 3 Sleep
- Stage 4 Sleep
- Stage of Exhaustion
- Stage of Resistance
- Stages of Moral Reasoning
- Standard Deviation
- Standardization
- Stanford Prison Experiment
- Stanley Milgram
- States of Consciousness
- Statistical Analysis
- Stereoblindness
- Stereotype
- Stimulant
- Stimulus Discrimination
- Stimulus Generalization
- Stimulus-based Stress
- Storage
- Strategic Family Therapy
- Stress
- Stress Management
- Stress Reduction
- Stressors
- Stroop Effect
- Structural Family Therapy
- Structuralism
- Studying
- Sublimation
- Subliminal Message
- Substance Abuse
- Substantia Nigra
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
- Suggestibility
- Suicidal Ideation
- Suicide
- Sulci
- Superego
- Supernatural
- Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
- Survey
- Sybil Eysenck
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Synapse
- Synaptic Vesicle
- Syntax
- Systematic Desensitization
- TAT
- TEMAS
- TEMAS Multicultural Thematic Apperception Test
- Taste
- Taste Aversion
- Taste Bud
- Telecommuting
- Telomere
- Temperament
- Temporal Lobe
- Temporal Theory of Pitch Perception
- Tension Headache
- Teratogen
- Terminal Button
- Thalamus
- Thematic Apperception Test
- Theory
- Theory X
- Theory Y
- Thermoception
- Theta Wave
- Thomas Holmes
- Thorndike
- Threshold of Excitation
- Thyroid Gland
- Timbre
- Token Economy
- Tolerance
- Tolman
- Top-down Processing
- Touch
- Trait
- Transactional Leadership Style
- Transduction
- Transference
- Transformational Leadership Style
- Transgender Hormone Therapy
- Transience
- Trauma
- Trial and Error
- Triangular Theory of Love
- Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
- Trichromatic Theory of Color Perception
- Trough
- Tuskegee Syphilis Study
- Tympanic Membrane
- Type B
- Type a
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity
- Umami
- Unconditional Positive Regard
- Unconditioned Response
- Unconditioned Stimulus
- Unconscious
- Uninvolved Parenting Style
- Vaccinations
- Validity
- Variable
- Variable Interval Schedule
- Variable Ratio Schedule
- Ventral Tegmental Area
- Ventricle
- Vertigo
- Vestibular Sense
- Vicarious Punishment
- Vicarious Reinforcement
- Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
- Visible Spectrum
- Vision
- Visual Encoding
- Voluntary Treatment
- Wakefulness
- Walter Cannon
- Walter Mischel
- Watson
- Wave
- Wavelength
- Wernicke's Area
- Wilhelm Wundt
- William James
- Withdrawal
- Wolfgang Köhler
- Work Stress
- Work Team
- Working Backwards
- Workplace Design
- Workplace Violence
- Work–family Balance
- Yale Attitude Change Approach
- Yerkes-Dodson
- Zygote
- –ology
Log in to add tags to this item.
- License:
- Creative Commons Attribution
- Language:
- English
Education Standards
OpenStax Psychology
Unit 1
Preface
Unit 2
Introduction to Psychology
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Psychology?
Lesson 3
History of Psychology
Lesson 4
Contemporary Psychology
Lesson 5
Careers in Psychology
Unit 3
Psychological Research
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Why Is Research Important?
Lesson 3
Approaches to Research
Lesson 4
Analyzing Findings
Lesson 5
Ethics
Unit 4
Biopsychology
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Human Genetics
Lesson 3
Cells of the Nervous System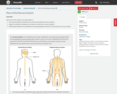
Lesson 4
Parts of the Nervous System
Lesson 5
The Brain and Spinal Cord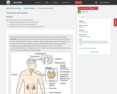
Lesson 6
The Endocrine System
Unit 5
States of Consciousness
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Consciousness?
Lesson 3
Sleep and Why We Sleep
Lesson 4
Stages of Sleep
Lesson 5
Sleep Problems and Disorders
Lesson 6
Substance Use and Abuse
Lesson 7
Other States of Consciousness
Unit 6
Sensation and Perception
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Sensation versus Perception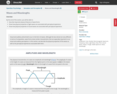
Lesson 3
Waves and Wavelengths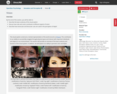
Lesson 4
Vision
Lesson 5
Hearing
Lesson 6
The Other Senses
Lesson 7
Gestalt Principles of Perception
Unit 7
Learning
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Learning?
Lesson 3
Classical Conditioning
Lesson 4
Operant Conditioning
Unit 8
Thinking and Intelligence
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Cognition?
Lesson 3
Language
Lesson 4
Problem Solving
Lesson 6
Measures of Intelligence
Lesson 7
The Source of Intelligence
Unit 9
Memory
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
How Memory Functions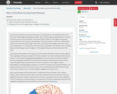
Lesson 4
Problems with Memory
Lesson 5
Ways to Enhance Memory
Unit 10
Lifespan Development
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Lifespan Development?
Lesson 3
Lifespan Theories
Lesson 4
Stages of Development
Lesson 5
Death and Dying
Unit 11
Emotion and Motivation
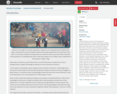
Lesson 1
Introduction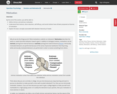
Lesson 2
Motivation
Lesson 3
Hunger and Eating
Lesson 4
Sexual Behavior
Lesson 5
Emotion
Unit 12
Personality
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Personality?
Lesson 5
Learning Approaches
Lesson 6
Humanistic Approaches
Lesson 7
Biological Approaches
Lesson 8
Trait Theorists
Lesson 10
Personality Assessment
Unit 13
Social Psychology
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Social Psychology?
Lesson 3
Self-presentation
Lesson 4
Attitudes and Persuasion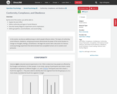
Lesson 6
Prejudice and Discrimination
Lesson 7
Aggression
Lesson 8
Prosocial Behavior
Unit 14
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Unit 15
Stress, Lifestyle, and Health
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Stress?
Lesson 3
Stressors
Lesson 4
Stress and Illness
Lesson 5
Regulation of Stress
Lesson 6
The Pursuit of Happiness
Unit 16
Psychological Disorders
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 5
Anxiety Disorders
Lesson 7
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Lesson 8
Mood Disorders
Lesson 9
Schizophrenia
Lesson 10
Dissociative Disorders
Lesson 11
Personality Disorders
Lesson 12
Disorders in Childhood
Unit 17
Therapy and Treatment